LEUKINE (sargramostim)
Office-Administration or Self-Administration
Diagnoses considered for coverage:
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Following Induction Chemotherapy – Indicated to shorten time to neutrophil recovery and to reduce the incidence of severe, life-threatening, or fatal infections following induction chemotherapy in adult patients 55 years and older with acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
- Autologous Peripheral Blood Progenitor Cell (PBPC) Mobilization and Collection – Indicated in adult patients with cancer undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for the mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells into peripheral blood for collection by leukapheresis.
- Autologous Peripheral Blood Progenitor Cell (PBPC) and Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) – Indicated for the acceleration of myeloid reconstitution following autologous PBPC or BMT in adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL).
- Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) – Indicated for the acceleration of myeloid reconstitution in adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older undergoing allogeneic bone marrow transplantation from HLA-matched related donors.
- Allogeneic or Autologous Bone Marrow Transplantation: Treatment of Delayed Neutrophil Recovery or Graft Failure – Indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 2 years and older who have undergone allogeneic or autologous bone marrow transplantation in whom neutrophil recovery is delayed or failed.
- Hematopoietic Syndrome of Acute Radiation Syndrome (H-ARS) – Indicated to increase survival in adult and pediatric patients from birth to 17 years of age acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation (Hematopoietic Syndrome of Acute Radiation Syndrome [H-ARS]).
Off Label Uses: - Febrile Neutropenia (FN), Prophylaxis – Has been used in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive anti-cancer drugs associated with a significant incidence of severe neutropenia with fever.
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-Related Neutropenia – Has been prescribed for HIV-related neutropenia.
- Treatment of High-Risk Febrile Neutropenia (FN) – Has been prescribed for the treatment of FN in patients who have received or are receiving myelosuppressive anticancer drugs associated with neutropenia who are at high risk for infection-associated complications.
Coverage Criteria:
For stem cell mobilization or bone marrow transplant (BMT):
- Dose does not exceed 250 mcg/m2/day; AND
- Prescribed by or in consultation with a hematologist or oncologist; AND
- Medical records document ONE of the following:
- Used for the mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells into the peripheral blood for collection by leukapheresis.
- Patient has had a peripheral stem cell transplant (PSCT) treated with myeloablative chemotherapy.
- Patient has a non-myeloid malignancy treated with myeloablative chemotherapy followed by allogeneic or autologous BMT; AND
- Requested GM-CSF agent will not be used in combination with other G-CSF/GM-CSF agents; AND
- One of the following:
- For requests prescribed through the medical benefit: no product preference
- For requests prescribed through the pharmacy benefit:
- Tried and failed, contraindicated, or intolerant to BOTH of the following:
- Nivestym
- Zarxio
- Tried and failed, contraindicated, or intolerant to BOTH of the following:
For prevention or reduction of neutropenia associated with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) following induction or consolidation chemotherapy (medical benefit only):
- Dose does not exceed 500 mcg/m2/day given intravenously (IV); AND
- Patient is 55 years of age or older; AND
- Prescribed by or in consultation with a hematologist or oncologist; AND
- Medical records document the patient has completed induction or consolidation chemotherapy for AML; AND
- Requested GM-CSF agent will not be used in combination with other G-CSF/GM-CSF agents.
For prophylaxis of febrile neutropenia (FN) or treatment of high-risk FN caused by myelosuppressive chemotherapy (off-label):
- Dose does not exceed 250 mcg/m2/day; AND
- Prescribed by or in consultation with a hematologist or oncologist; AND
- Medical records document ONE of the following:
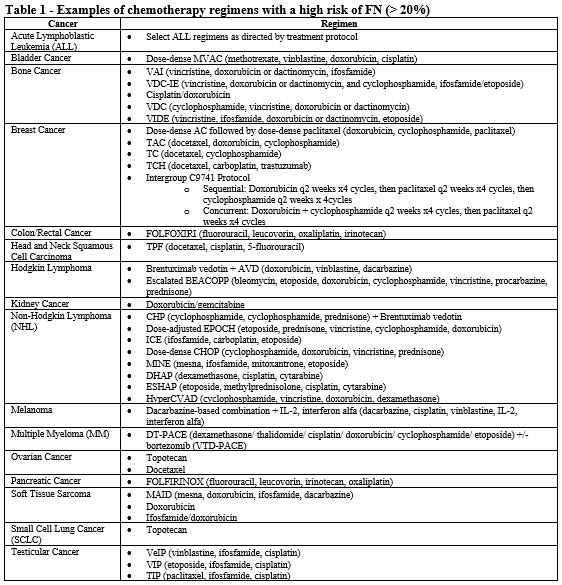
- Patient is receiving chemotherapy regimen(s) associated with greater than 20% incidence of FN (see Table 1).
- All of the following:
- Diagnosis of acute febrile neutropenia (FN).
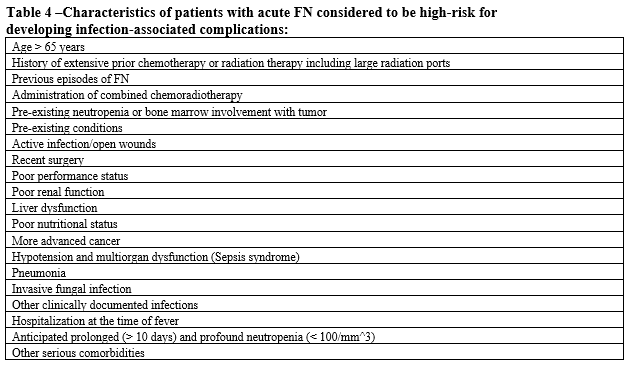
- Patient is at high risk for infection-associated complications (see Table 4).
- Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) is less than 1000 cells/mm3.
- Both of the following:
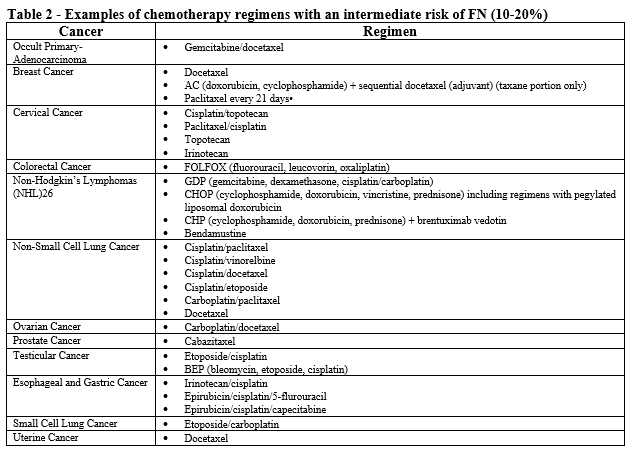
- Patient is receiving chemotherapy regimen(s) associated with 10-20% incidence of FN (see Table 2).
- Patient has one or more risk factors associated with chemotherapy induced infection, FN, or neutropenia.
- Both of the following:
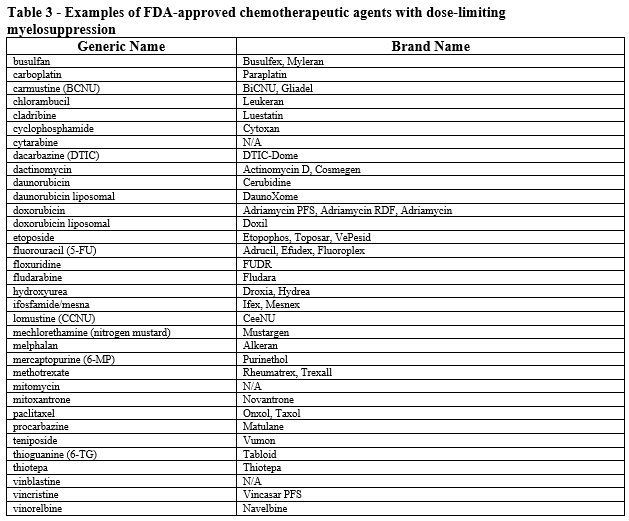
- Patient is receiving myelosuppressive anticancer drugs associated with neutropenia (see Table 3).
- Patient has a history of FN or dose-limiting event during a previous course of chemotherapy (i.e., secondary prophylaxis); AND
- Requested GM-CSF agent will not be used in combination with other G-CSF/GM-CSF agents; AND
- One of the following:
- For requests prescribed through the medical benefit: no product preference
- For requests prescribed through the pharmacy benefit:
- Tried and failed, contraindicated, or intolerant to BOTH of the following:
- Nivestym
- Zarxio
- Tried and failed, contraindicated, or intolerant to BOTH of the following:
For prevention or treatment of acute radiation syndrome (ARS) neutropenia:
- Dose does not exceed recommended FDA-maximum of:
- Adults and pediatric patients weighing greater than 40 kg: 7 mcg/kg/day
- Pediatric patients 15 kg to 40 kg: 10 mcg/kg/day
- Pediatric patients less than 15 kg: 12 mcg/kg/day; AND
- Prescribed by or in consultation with a radiologist, hematologist or oncologist; AND
- Medical records document the patient was, or will be, exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation; AND
- Requested GM-CSF agent will not be used in combination with other G-CSF/GM-CSF agents; AND
- One of the following:
- For requests prescribed through the medical benefit: no product preference
- For requests prescribed through the pharmacy benefit:
- Tried and failed, contraindicated, or intolerant to BOTH of the following:
- Nivestym
- Zarxio
- Tried and failed, contraindicated, or intolerant to BOTH of the following:
For diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-related neutropenia (off-label):
- Dose does not exceed the recommended dose of 250 mcg/m2/day; AND
- Prescribed by or in consultation with a hematologist, oncologist, or infectious disease specialist; AND
- Patient has documented HIV with absolute neutrophil count (ANC) less than or equal to 1,000 cells/mm3; AND
- Requested GM-CSF agent will not be used in combination with other G-CSF/GM-CSF agents; AND
- One of the following:
- For requests prescribed through the medical benefit: no product preference
- For requests prescribed through the pharmacy benefit:
- Tried and failed, contraindicated, or intolerant to BOTH of the following:
- Nivestym
- Zarxio
- Tried and failed, contraindicated, or intolerant to BOTH of the following:
Reauthorization Criteria:
For prophylaxis of febrile neutropenia (FN) or treatment of high-risk FN caused by myelosuppressive chemotherapy (off-label):
- Dose does not exceed 250 mcg/m2/day; AND
- Medical records document the patient continues to receive myelosuppressive chemotherapy; AND
- Requested GM-CSF agent will not be used in combination with other G-CSF/GM-CSF agents.
For diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-related neutropenia (off-label):
- Dose does not exceed the recommended dose of 250 mcg/m2/day; AND
- Medical records document the patient’s absolute neutrophil count (ANC) has stabilized while on GM-CSF therapy; AND
- Requested GM-CSF agent will not be used in combination with other G-CSF/GM-CSF agents.
Coverage Duration:
- BMT: 2 months
- AML: 2 months
- FN prophylaxis or high-risk FN treatment
- Initial: 3 months
- Reauthorization: duration of chemotherapy
- ARS: 1 month
- HIV-related neutropenia
- Initial: 6 months
- Reauthorization: 6 months
Authorization is not covered for the following:
- The use of this drug for indications not listed in this policy does not meet the coverage criteria established by the Western Health Advantage (WHA) Pharmacy and Therapeutics (P&T) Committee.
Additional Information:
- Dose dense chemotherapy is a treatment plan in which drugs are given with less time between treatments than in a standard chemotherapy treatment plan.
- Leukine used for the prophylaxis of febrile neutropenia in AML following induction chemotherapy is administered as 250 mcg/m2/day intravenously (IV) over a 4-hour period starting approximately on day 11 or four days following the completion of induction chemotherapy, if the day 10 bone marrow is hypoplastic with less than 5% blasts. Continue Leukine until an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) greater than 1500 cells/mm3 for 3 consecutive days or a maximum of 42 days.
- FN is described by clinical practice guidelines as neutropenia with a single oral or tympanic temperature greater than or equal to 101°F (38.3°C) or greater than or equal to 100.4°F (38°C) for at least one hour.
- The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) guidelines recommend against their use for all patients with established fever and neutropenia, whereas the American Society of Clinical Oncology and National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines state that their use can be "considered" for patients at high risk for infection-associated complications or who have prognostic factors that are predictive of a poor clinical outcome
- Non-myeloid malignancies are cancers that are not classified as: (1) myelodysplastic syndromes (MDSs); (2) myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs); (3) myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms (MDS/MPN); or (4) myeloid malignancies associated with eosinophilia and abnormalities of growth factor receptors derived from platelets or fibroblasts.
- Bone marrow transplants are most commonly used in the following diseases: leukemias, lymphomas, multiple myeloma, immune deficiency disorders, severe aplastic anemia, and some solid-tumor cancers (in rare circumstances).
- Hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) or hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are cells present in blood and bone marrow. HPCs are capable of forming mature blood cells, such as red blood cells (the cells that carry oxygen), platelets (the cells that help stop bleeding) and white blood cells (the cells that fight infections). Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is the IV infusion of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells designed to establish marrow and immune function in patients with a variety of acquired and inherited malignant and nonmalignant disorders.
- Allogeneic stem cell transplantation involves transferring the stem cells from a healthy person (the donor) to the patient’s body after high-intensity chemotherapy or radiation. The donated stem cells can come from either a related or an unrelated donor.
- An autologous stem cell transplant uses healthy blood stem cells from your own body to replace your diseased or damaged bone marrow. An autologous stem cell transplant is also called an autologous bone marrow transplant.
- One cubic millimeter (mm^3) = One microliter (µL).
- Meters squared (m2) is the unit used to describe body surface area (BSA). The calculation is derived from height and weight measurements. A calculator to determine BSA can be found at http://www.medcalc.com/body.html or https://www.calculator.net/body-surface-area-calculator.html
Review History:
02/15/2022 - New policy approved by P&T.
References:
- Beveridge RA, Miller JA, Kales AN, et al. A comparison of efficacy of sargramostim (yeast-derived RhuGM-CSF) and filgrastim (bacteria-derived RhuG-CSF) in the therapeutic setting of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression. Cancer Invest. 1998;16(6):366-373.
- Beveridge RA, Miller JA, Kales AN, et al. Randomized trial comparing the tolerability of sargramostim (yeast-derived RhuGM-CSF) and filgrastim (bacteria-derived RhuG-CSF) in cancer patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Support Care Cancer. 1997 Jul;5(4):289-298.
- DRUGDEX® System [Internet database]. Greenwood Village, Colo: Thomson Healthcare. Updated periodically. Accessed February 7, 2022.
- Leukine Prescribing Information. sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC. Bridgewater, NJ. March 2018.
- Lucas AJ, Olin JL, Coleman MD. Management and preventive measures for febrile neutropenia. Pharmacy and Therapeutics. 2018 Apr;43(4):228.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Hematopoietic Growth Factors. Version 1.2022. Available at: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/growthfactors.pdf Accessed February 7, 2022.
- Weaver CH, Schulman KA, Wilson-Relyea B, et al. Randomized trial of filgrastim, sargramostim, or sequential sargramostim and filgrastim after myelosuppressive chemotherapy for the harvesting of peripheral-blood stem cells. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:43-53.
Last review date: February 15, 2022

